Location
Location ANSS
The ANSS event ID is nn00523848 and the event page is at
https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/nn00523848/executive.
2015/12/24 20:30:38 41.881 -119.594 11.3 4.4 Nevada
Focal Mechanism
USGS/SLU Moment Tensor Solution
ENS 2015/12/24 20:30:38:0 41.88 -119.59 11.3 4.4 Nevada
Stations used:
BK.WDC IM.NV31 IW.MFID LB.BMN LB.TPH NC.KCPB NC.KHMB NC.KMR
NN.COLR NN.CTC NN.EMB NN.KVN NN.LCH NN.LHV NN.MPK NN.PAH
NN.PNT NN.REDF NN.RYN NN.VCN NN.WDEM NN.YER TA.R11A UO.BUCK
UO.PINE US.BMO US.HAWA US.HLID US.WVOR UW.BLOW UW.CCRK
UW.DDRF UW.HOOD UW.IRON UW.TREE UW.TUCA UW.UMAT
Filtering commands used:
cut o DIST/3.3 -30 o DIST/3.3 +70
rtr
taper w 0.1
hp c 0.03 n 3
lp c 0.10 n 3
br c 0.12 0.25 n 4 p 2
Best Fitting Double Couple
Mo = 1.04e+23 dyne-cm
Mw = 4.61
Z = 6 km
Plane Strike Dip Rake
NP1 60 70 -35
NP2 163 57 -156
Principal Axes:
Axis Value Plunge Azimuth
T 1.04e+23 8 114
N 0.00e+00 50 214
P -1.04e+23 39 18
Moment Tensor: (dyne-cm)
Component Value
Mxx -4.04e+22
Mxy -5.64e+22
Mxz -5.39e+22
Myy 7.85e+22
Myz -2.37e+21
Mzz -3.82e+22
#-------------
####------------------
######----------------------
######----------- ----------
########----------- P ------------
#########----------- -------------
##########--------------------------##
###########-------------------------####
###########-----------------------######
############---------------------#########
############-------------------###########
#############----------------#############
#############-------------################
#############---------##################
##############-----################# #
################################### T
#####--------#####################
--------------####################
-------------#################
--------------##############
-------------#########
------------##
Global CMT Convention Moment Tensor:
R T P
-3.82e+22 -5.39e+22 2.37e+21
-5.39e+22 -4.04e+22 5.64e+22
2.37e+21 5.64e+22 7.85e+22
Details of the solution is found at
http://www.eas.slu.edu/eqc/eqc_mt/MECH.NA/20151224203038/index.html
|
Preferred Solution
The preferred solution from an analysis of the surface-wave spectral amplitude radiation pattern, waveform inversion or first motion observations is
STK = 60
DIP = 70
RAKE = -35
MW = 4.61
HS = 6.0
The NDK file is 20151224203038.ndk
The waveform inversion is preferred.
Moment Tensor Comparison
The following compares this source inversion to those provided by others. The purpose is to look for major differences and also to note slight differences that might be inherent to the processing procedure. For completeness the USGS/SLU solution is repeated from above.
| SLU |
USGSMT |
USGS/SLU Moment Tensor Solution
ENS 2015/12/24 20:30:38:0 41.88 -119.59 11.3 4.4 Nevada
Stations used:
BK.WDC IM.NV31 IW.MFID LB.BMN LB.TPH NC.KCPB NC.KHMB NC.KMR
NN.COLR NN.CTC NN.EMB NN.KVN NN.LCH NN.LHV NN.MPK NN.PAH
NN.PNT NN.REDF NN.RYN NN.VCN NN.WDEM NN.YER TA.R11A UO.BUCK
UO.PINE US.BMO US.HAWA US.HLID US.WVOR UW.BLOW UW.CCRK
UW.DDRF UW.HOOD UW.IRON UW.TREE UW.TUCA UW.UMAT
Filtering commands used:
cut o DIST/3.3 -30 o DIST/3.3 +70
rtr
taper w 0.1
hp c 0.03 n 3
lp c 0.10 n 3
br c 0.12 0.25 n 4 p 2
Best Fitting Double Couple
Mo = 1.04e+23 dyne-cm
Mw = 4.61
Z = 6 km
Plane Strike Dip Rake
NP1 60 70 -35
NP2 163 57 -156
Principal Axes:
Axis Value Plunge Azimuth
T 1.04e+23 8 114
N 0.00e+00 50 214
P -1.04e+23 39 18
Moment Tensor: (dyne-cm)
Component Value
Mxx -4.04e+22
Mxy -5.64e+22
Mxz -5.39e+22
Myy 7.85e+22
Myz -2.37e+21
Mzz -3.82e+22
#-------------
####------------------
######----------------------
######----------- ----------
########----------- P ------------
#########----------- -------------
##########--------------------------##
###########-------------------------####
###########-----------------------######
############---------------------#########
############-------------------###########
#############----------------#############
#############-------------################
#############---------##################
##############-----################# #
################################### T
#####--------#####################
--------------####################
-------------#################
--------------##############
-------------#########
------------##
Global CMT Convention Moment Tensor:
R T P
-3.82e+22 -5.39e+22 2.37e+21
-5.39e+22 -4.04e+22 5.64e+22
2.37e+21 5.64e+22 7.85e+22
Details of the solution is found at
http://www.eas.slu.edu/eqc/eqc_mt/MECH.NA/20151224203038/index.html
|
Regional Moment Tensor (Mwr)
Moment 1.196e+16 N-m
Magnitude 4.65
Depth 6.0 km
Percent DC 97%
Half Duration –
Catalog US (us100049cn)
Data Source US2
Contributor US2
Nodal Planes
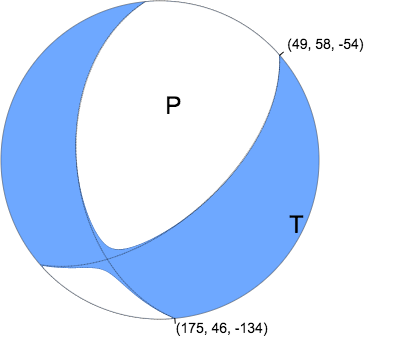
Plane Strike Dip Rake
NP1 49 58 -54
NP2 175 46 -134
Principal Axes
Axis Value Plunge Azimuth
T 1.187 7 114
N 0.018 30 208
P -1.205 59 13
|
Magnitudes
Given the availability of digital waveforms for determination of the moment tensor, this section documents the added processing leading to mLg, if appropriate to the region, and ML by application of the respective IASPEI formulae. As a research study, the linear distance term of the IASPEI formula
for ML is adjusted to remove a linear distance trend in residuals to give a regionally defined ML. The defined ML uses horizontal component recordings, but the same procedure is applied to the vertical components since there may be some interest in vertical component ground motions. Residual plots versus distance may indicate interesting features of ground motion scaling in some distance ranges. A residual plot of the regionalized magnitude is given as a function of distance and azimuth, since data sets may transcend different wave propagation provinces.
ML Magnitude
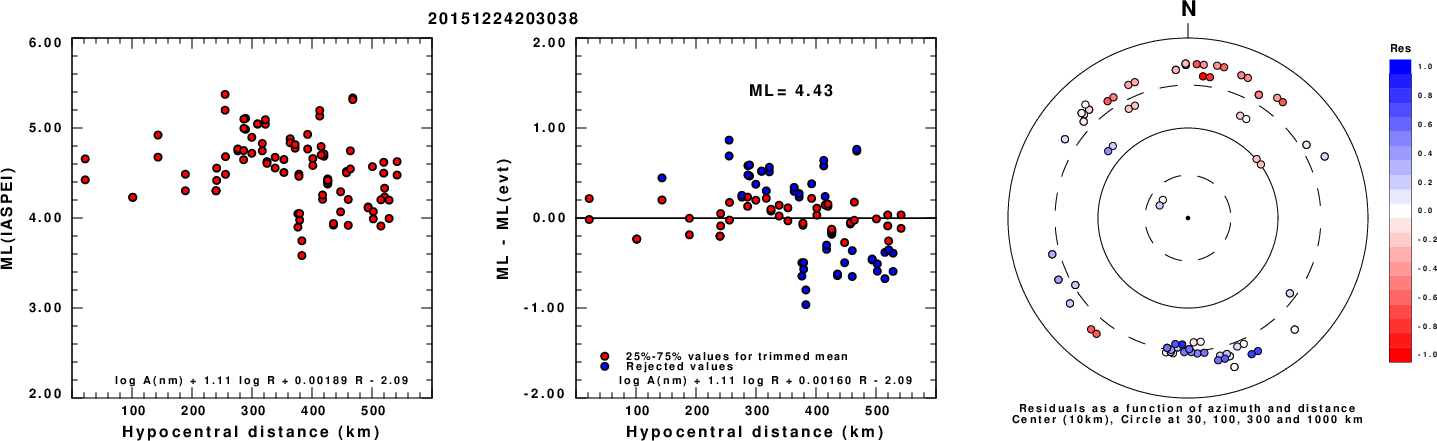
Left: ML computed using the IASPEI formula for Horizontal components. Center: ML residuals computed using a modified IASPEI formula that accounts for path specific attenuation; the values used for the trimmed mean are indicated. The ML relation used for each figure is given at the bottom of each plot.
Right: Residuals from new relation as a function of distance and azimuth.
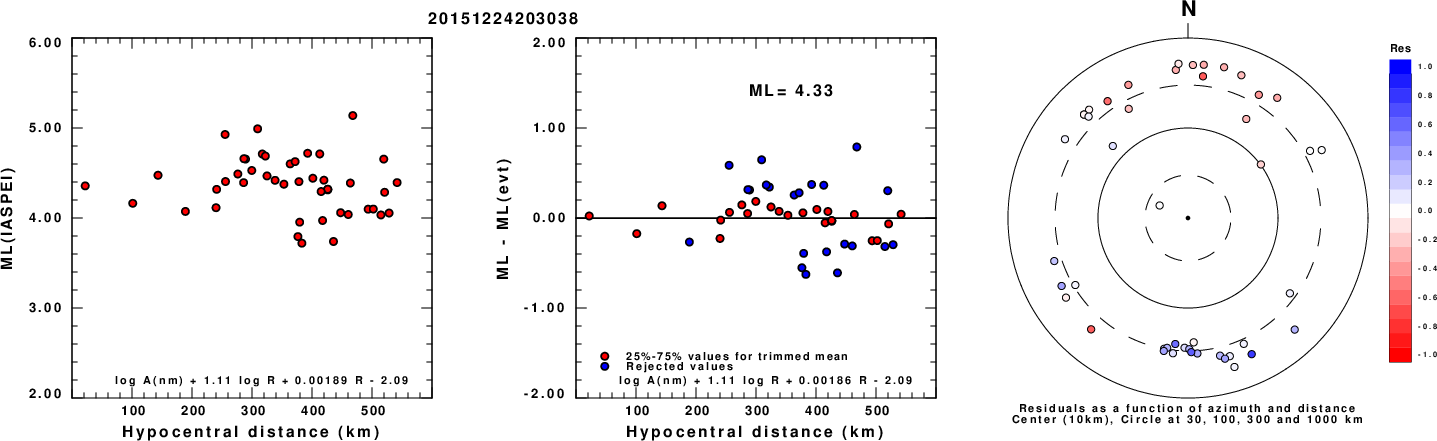
Left: ML computed using the IASPEI formula for Vertical components (research). Center: ML residuals computed using a modified IASPEI formula that accounts for path specific attenuation; the values used for the trimmed mean are indicated. The ML relation used for each figure is given at the bottom of each plot.
Right: Residuals from new relation as a function of distance and azimuth.
Context
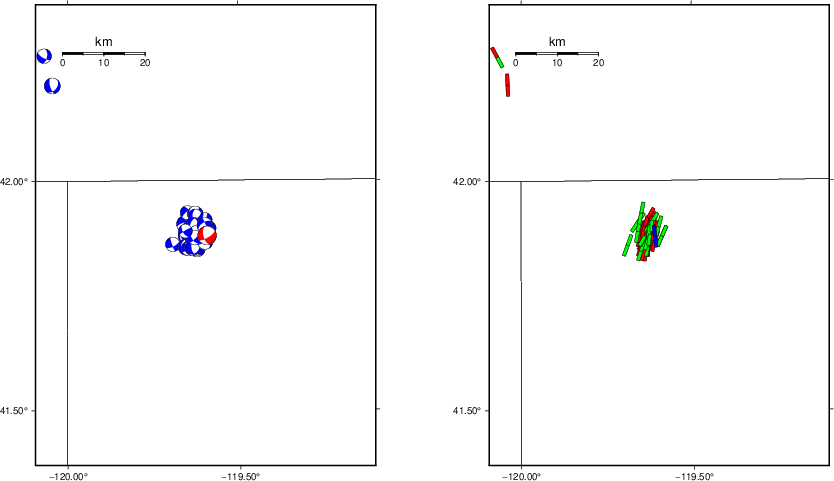
The left panel of the next figure presents the focal mechanism for this earthquake (red) in the context of other nearby events (blue) in the SLU Moment Tensor Catalog. The right panel shows the inferred direction of maximum compressive stress and the type of faulting (green is strike-slip, red is normal, blue is thrust; oblique is shown by a combination of colors). Thus context plot is useful for assessing the appropriateness of the moment tensor of this event.
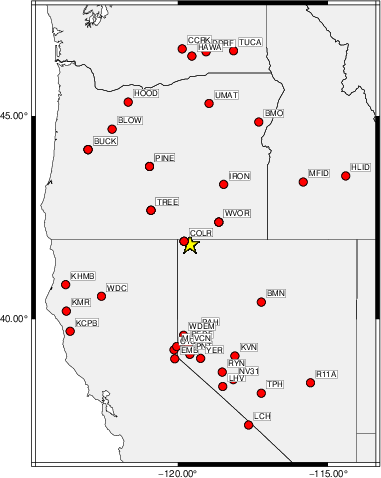
Waveform Inversion using wvfgrd96
The focal mechanism was determined using broadband seismic waveforms. The location of the event (star) and the
stations used for (red) the waveform inversion are shown in the next figure.
|
|
Location of broadband stations used for waveform inversion
|
The program wvfgrd96 was used with good traces observed at short distance to determine the focal mechanism, depth and seismic moment. This technique requires a high quality signal and well determined velocity model for the Green's functions. To the extent that these are the quality data, this type of mechanism should be preferred over the radiation pattern technique which requires the separate step of defining the pressure and tension quadrants and the correct strike.
The observed and predicted traces are filtered using the following gsac commands:
cut o DIST/3.3 -30 o DIST/3.3 +70
rtr
taper w 0.1
hp c 0.03 n 3
lp c 0.10 n 3
br c 0.12 0.25 n 4 p 2
The results of this grid search are as follow:
DEPTH STK DIP RAKE MW FIT
WVFGRD96 1.0 255 85 15 4.37 0.4740
WVFGRD96 2.0 70 90 -25 4.50 0.6450
WVFGRD96 3.0 250 90 35 4.55 0.7355
WVFGRD96 4.0 60 75 -40 4.58 0.7911
WVFGRD96 5.0 60 70 -40 4.60 0.8132
WVFGRD96 6.0 60 70 -35 4.61 0.8137
WVFGRD96 7.0 65 85 -25 4.60 0.8065
WVFGRD96 8.0 60 75 -35 4.65 0.8014
WVFGRD96 9.0 245 90 25 4.64 0.7946
WVFGRD96 10.0 245 85 25 4.64 0.7869
WVFGRD96 11.0 245 80 20 4.65 0.7787
WVFGRD96 12.0 245 80 20 4.66 0.7681
WVFGRD96 13.0 245 80 20 4.67 0.7551
WVFGRD96 14.0 245 80 20 4.68 0.7421
WVFGRD96 15.0 245 80 25 4.69 0.7259
WVFGRD96 16.0 245 80 25 4.70 0.7121
WVFGRD96 17.0 245 80 25 4.71 0.6954
WVFGRD96 18.0 245 75 25 4.72 0.6814
WVFGRD96 19.0 245 75 25 4.73 0.6654
WVFGRD96 20.0 245 75 30 4.74 0.6499
WVFGRD96 21.0 245 75 30 4.75 0.6349
WVFGRD96 22.0 245 75 30 4.76 0.6189
WVFGRD96 23.0 250 70 35 4.77 0.6028
WVFGRD96 24.0 250 70 35 4.77 0.5875
WVFGRD96 25.0 250 70 35 4.78 0.5719
WVFGRD96 26.0 250 65 40 4.79 0.5565
WVFGRD96 27.0 250 65 40 4.80 0.5423
WVFGRD96 28.0 250 65 40 4.81 0.5278
WVFGRD96 29.0 250 65 40 4.81 0.5132
The best solution is
WVFGRD96 6.0 60 70 -35 4.61 0.8137
The mechanism corresponding to the best fit is
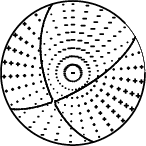
|
|
Figure 1. Waveform inversion focal mechanism
|
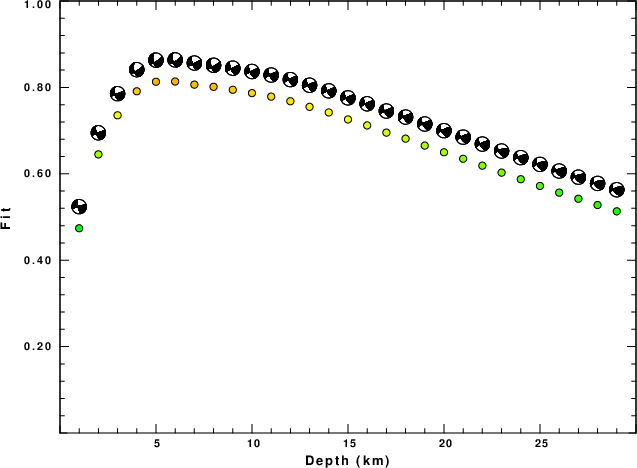
The best fit as a function of depth is given in the following figure:
|
|
Figure 2. Depth sensitivity for waveform mechanism
|
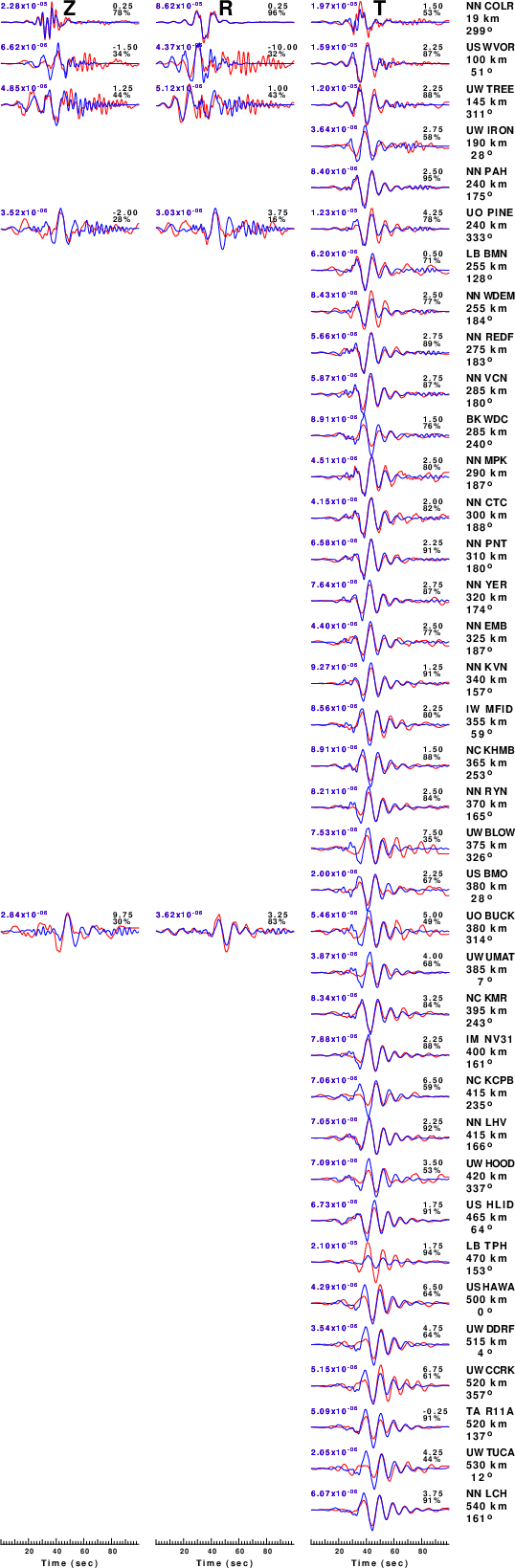
The comparison of the observed and predicted waveforms is given in the next figure. The red traces are the observed and the blue are the predicted.
Each observed-predicted component is plotted to the same scale and peak amplitudes are indicated by the numbers to the left of each trace. A pair of numbers is given in black at the right of each predicted traces. The upper number it the time shift required for maximum correlation between the observed and predicted traces. This time shift is required because the synthetics are not computed at exactly the same distance as the observed, the velocity model used in the predictions may not be perfect and the epicentral parameters may be be off.
A positive time shift indicates that the prediction is too fast and should be delayed to match the observed trace (shift to the right in this figure). A negative value indicates that the prediction is too slow. The lower number gives the percentage of variance reduction to characterize the individual goodness of fit (100% indicates a perfect fit).
The bandpass filter used in the processing and for the display was
cut o DIST/3.3 -30 o DIST/3.3 +70
rtr
taper w 0.1
hp c 0.03 n 3
lp c 0.10 n 3
br c 0.12 0.25 n 4 p 2
|
|
Figure 3. Waveform comparison for selected depth. Red: observed; Blue - predicted. The time shift with respect to the model prediction is indicated. The percent of fit is also indicated. The time scale is relative to the first trace sample.
|
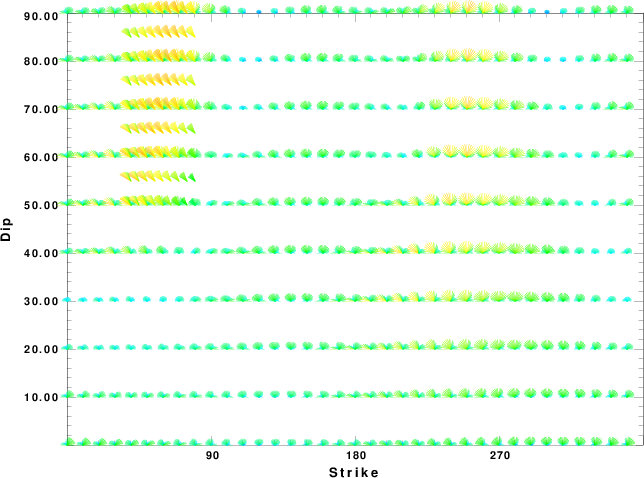
|
|
Focal mechanism sensitivity at the preferred depth. The red color indicates a very good fit to the waveforms.
Each solution is plotted as a vector at a given value of strike and dip with the angle of the vector representing the rake angle, measured, with respect to the upward vertical (N) in the figure.
|
A check on the assumed source location is possible by looking at the time shifts between the observed and predicted traces. The time shifts for waveform matching arise for several reasons:
- The origin time and epicentral distance are incorrect
- The velocity model used for the inversion is incorrect
- The velocity model used to define the P-arrival time is not the
same as the velocity model used for the waveform inversion
(assuming that the initial trace alignment is based on the
P arrival time)
Assuming only a mislocation, the time shifts are fit to a functional form:
Time_shift = A + B cos Azimuth + C Sin Azimuth
The time shifts for this inversion lead to the next figure:
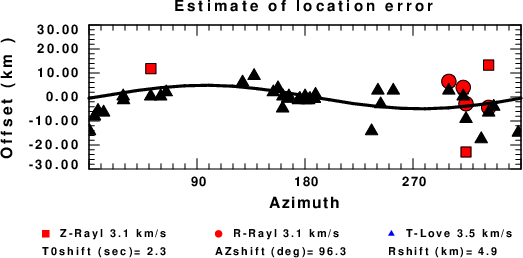
The derived shift in origin time and epicentral coordinates are given at the bottom of the figure.
Velocity Model
The WUS.model used for the waveform synthetic seismograms and for the surface wave eigenfunctions and dispersion is as follows
(The format is in the model96 format of Computer Programs in Seismology).
MODEL.01
Model after 8 iterations
ISOTROPIC
KGS
FLAT EARTH
1-D
CONSTANT VELOCITY
LINE08
LINE09
LINE10
LINE11
H(KM) VP(KM/S) VS(KM/S) RHO(GM/CC) QP QS ETAP ETAS FREFP FREFS
1.9000 3.4065 2.0089 2.2150 0.302E-02 0.679E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
6.1000 5.5445 3.2953 2.6089 0.349E-02 0.784E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
13.0000 6.2708 3.7396 2.7812 0.212E-02 0.476E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
19.0000 6.4075 3.7680 2.8223 0.111E-02 0.249E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
0.0000 7.9000 4.6200 3.2760 0.164E-10 0.370E-10 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
Last Changed Sat Apr 27 01:48:47 AM CDT 2024