Location
Location ANSS
The ANSS event ID is usc000gp07 and the event page is at
https://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/eventpage/usc000gp07/executive.
2013/05/06 03:20:56 42.642 -111.998 5.0 3.5 Idaho
Focal Mechanism
USGS/SLU Moment Tensor Solution
ENS 2013/05/06 03:20:56:0 42.64 -112.00 5.0 3.5 Idaho
Stations used:
IW.FLWY IW.FXWY IW.IMW IW.LOHW IW.MOOW IW.REDW IW.SNOW
IW.TPAW LB.BMN TA.H17A TA.R11A US.AHID US.BW06 US.DUG
US.HLID US.HWUT US.RLMT UU.BGU UU.HVU UU.JLU UU.MPU UU.SPU
UU.SZCU WY.YFT WY.YHB WY.YNR WY.YPP WY.YUF
Filtering commands used:
hp c 0.02 n 3
lp c 0.10 n 3
Best Fitting Double Couple
Mo = 2.40e+21 dyne-cm
Mw = 3.52
Z = 13 km
Plane Strike Dip Rake
NP1 339 77 -98
NP2 190 15 -60
Principal Axes:
Axis Value Plunge Azimuth
T 2.40e+21 32 75
N 0.00e+00 7 341
P -2.40e+21 57 239
Moment Tensor: (dyne-cm)
Component Value
Mxx -7.49e+19
Mxy 1.14e+20
Mxz 8.29e+20
Myy 1.11e+21
Myz 1.97e+21
Mzz -1.04e+21
---###########
###--#################
####------##################
###---------##################
###------------###################
###--------------###################
###----------------###################
###------------------########### #####
###-------------------########## T #####
###--------------------########## ######
###---------------------##################
###----------------------#################
###--------- ----------#################
##--------- P -----------###############
###-------- ------------##############
###----------------------#############
##-----------------------###########
##----------------------##########
##--------------------########
##-------------------#######
##----------------####
#-------------
Global CMT Convention Moment Tensor:
R T P
-1.04e+21 8.29e+20 -1.97e+21
8.29e+20 -7.49e+19 -1.14e+20
-1.97e+21 -1.14e+20 1.11e+21
Details of the solution is found at
http://www.eas.slu.edu/eqc/eqc_mt/MECH.NA/20130506032056/index.html
|
Preferred Solution
The preferred solution from an analysis of the surface-wave spectral amplitude radiation pattern, waveform inversion or first motion observations is
STK = 190
DIP = 15
RAKE = -60
MW = 3.52
HS = 13.0
The NDK file is 20130506032056.ndk
The waveform inversion is preferred.
Magnitudes
Given the availability of digital waveforms for determination of the moment tensor, this section documents the added processing leading to mLg, if appropriate to the region, and ML by application of the respective IASPEI formulae. As a research study, the linear distance term of the IASPEI formula
for ML is adjusted to remove a linear distance trend in residuals to give a regionally defined ML. The defined ML uses horizontal component recordings, but the same procedure is applied to the vertical components since there may be some interest in vertical component ground motions. Residual plots versus distance may indicate interesting features of ground motion scaling in some distance ranges. A residual plot of the regionalized magnitude is given as a function of distance and azimuth, since data sets may transcend different wave propagation provinces.
ML Magnitude
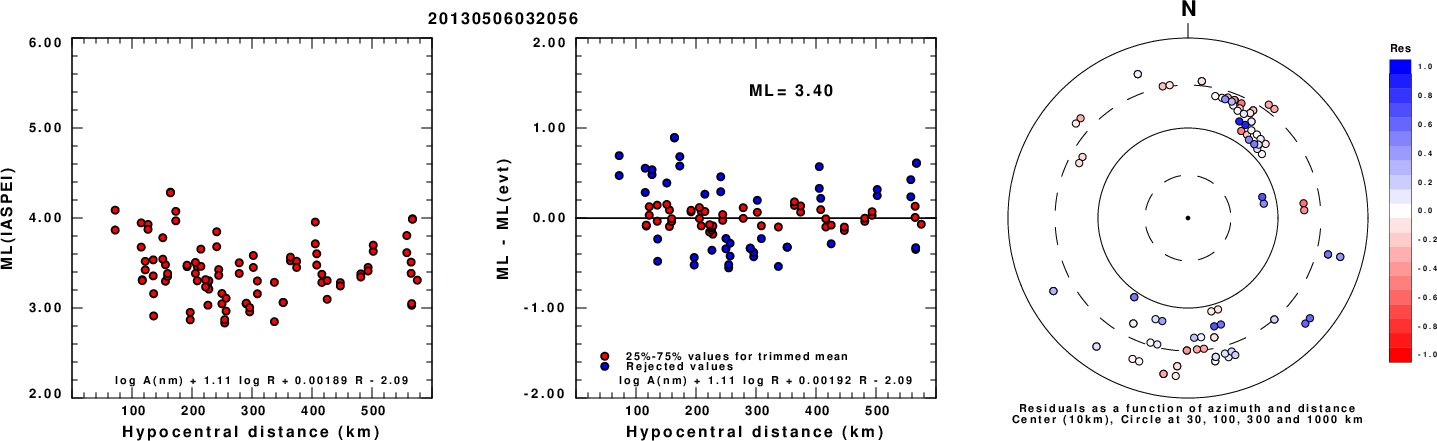
Left: ML computed using the IASPEI formula for Horizontal components. Center: ML residuals computed using a modified IASPEI formula that accounts for path specific attenuation; the values used for the trimmed mean are indicated. The ML relation used for each figure is given at the bottom of each plot.
Right: Residuals from new relation as a function of distance and azimuth.
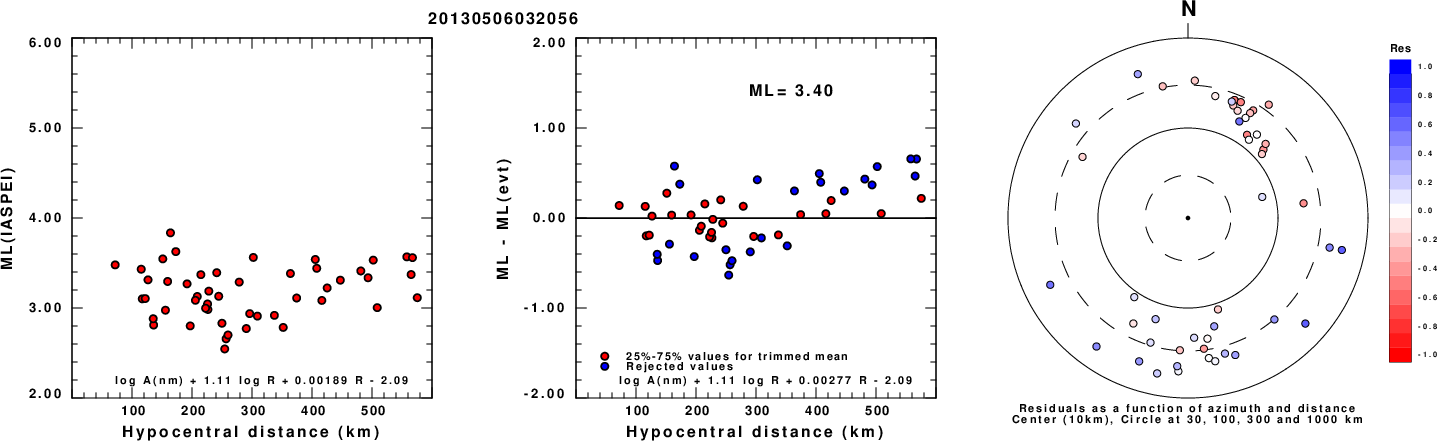
Left: ML computed using the IASPEI formula for Vertical components (research). Center: ML residuals computed using a modified IASPEI formula that accounts for path specific attenuation; the values used for the trimmed mean are indicated. The ML relation used for each figure is given at the bottom of each plot.
Right: Residuals from new relation as a function of distance and azimuth.
Context
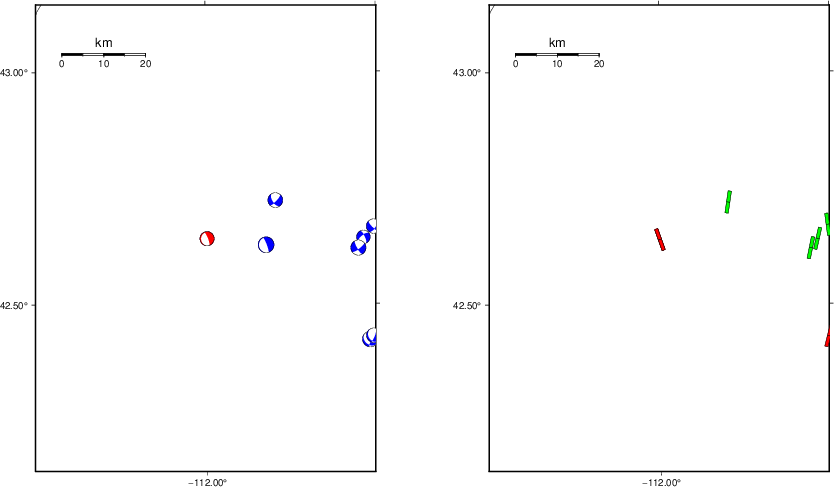
The left panel of the next figure presents the focal mechanism for this earthquake (red) in the context of other nearby events (blue) in the SLU Moment Tensor Catalog. The right panel shows the inferred direction of maximum compressive stress and the type of faulting (green is strike-slip, red is normal, blue is thrust; oblique is shown by a combination of colors). Thus context plot is useful for assessing the appropriateness of the moment tensor of this event.
Waveform Inversion using wvfgrd96
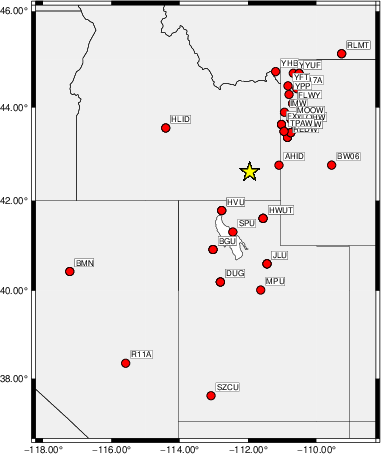
The focal mechanism was determined using broadband seismic waveforms. The location of the event (star) and the
stations used for (red) the waveform inversion are shown in the next figure.
|
|
Location of broadband stations used for waveform inversion
|
The program wvfgrd96 was used with good traces observed at short distance to determine the focal mechanism, depth and seismic moment. This technique requires a high quality signal and well determined velocity model for the Green's functions. To the extent that these are the quality data, this type of mechanism should be preferred over the radiation pattern technique which requires the separate step of defining the pressure and tension quadrants and the correct strike.
The observed and predicted traces are filtered using the following gsac commands:
hp c 0.02 n 3
lp c 0.10 n 3
The results of this grid search are as follow:
DEPTH STK DIP RAKE MW FIT
WVFGRD96 0.5 145 45 90 3.13 0.3580
WVFGRD96 1.0 295 50 65 3.17 0.3097
WVFGRD96 2.0 140 45 85 3.30 0.3542
WVFGRD96 3.0 90 30 35 3.32 0.2530
WVFGRD96 4.0 245 20 5 3.32 0.3022
WVFGRD96 5.0 235 20 -5 3.33 0.3685
WVFGRD96 6.0 230 20 -15 3.35 0.4221
WVFGRD96 7.0 225 20 -25 3.36 0.4621
WVFGRD96 8.0 215 15 -30 3.44 0.4856
WVFGRD96 9.0 210 15 -40 3.46 0.5152
WVFGRD96 10.0 200 15 -50 3.48 0.5367
WVFGRD96 11.0 195 15 -55 3.49 0.5517
WVFGRD96 12.0 190 15 -60 3.51 0.5603
WVFGRD96 13.0 190 15 -60 3.52 0.5635
WVFGRD96 14.0 180 15 -70 3.53 0.5619
WVFGRD96 15.0 345 80 -90 3.55 0.5572
WVFGRD96 16.0 165 10 -90 3.57 0.5494
WVFGRD96 17.0 160 10 -95 3.58 0.5384
WVFGRD96 18.0 155 10 -95 3.58 0.5255
WVFGRD96 19.0 185 10 -65 3.59 0.5108
WVFGRD96 20.0 190 10 -60 3.60 0.4951
WVFGRD96 21.0 190 10 -60 3.61 0.4786
WVFGRD96 22.0 170 5 -80 3.62 0.4608
WVFGRD96 23.0 145 90 70 3.61 0.4418
WVFGRD96 24.0 145 90 70 3.62 0.4258
WVFGRD96 25.0 145 90 70 3.63 0.4094
WVFGRD96 26.0 145 90 70 3.64 0.3923
WVFGRD96 27.0 140 90 70 3.64 0.3745
WVFGRD96 28.0 140 90 70 3.65 0.3566
WVFGRD96 29.0 320 90 -70 3.65 0.3380
The best solution is
WVFGRD96 13.0 190 15 -60 3.52 0.5635
The mechanism corresponding to the best fit is
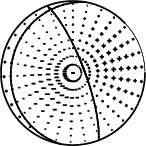
|
|
Figure 1. Waveform inversion focal mechanism
|
The best fit as a function of depth is given in the following figure:
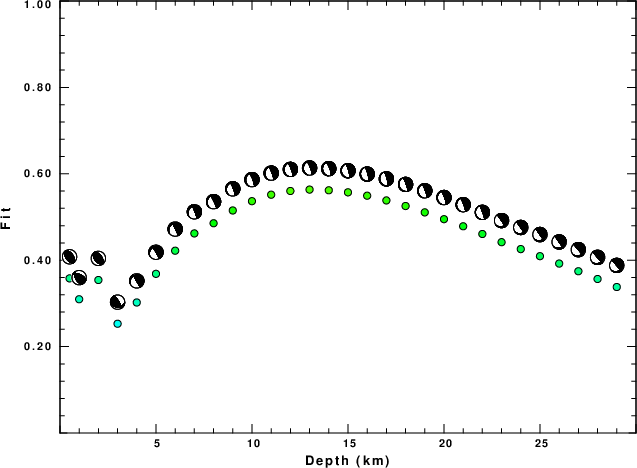
|
|
Figure 2. Depth sensitivity for waveform mechanism
|
The comparison of the observed and predicted waveforms is given in the next figure. The red traces are the observed and the blue are the predicted.
Each observed-predicted component is plotted to the same scale and peak amplitudes are indicated by the numbers to the left of each trace. A pair of numbers is given in black at the right of each predicted traces. The upper number it the time shift required for maximum correlation between the observed and predicted traces. This time shift is required because the synthetics are not computed at exactly the same distance as the observed, the velocity model used in the predictions may not be perfect and the epicentral parameters may be be off.
A positive time shift indicates that the prediction is too fast and should be delayed to match the observed trace (shift to the right in this figure). A negative value indicates that the prediction is too slow. The lower number gives the percentage of variance reduction to characterize the individual goodness of fit (100% indicates a perfect fit).
The bandpass filter used in the processing and for the display was
hp c 0.02 n 3
lp c 0.10 n 3
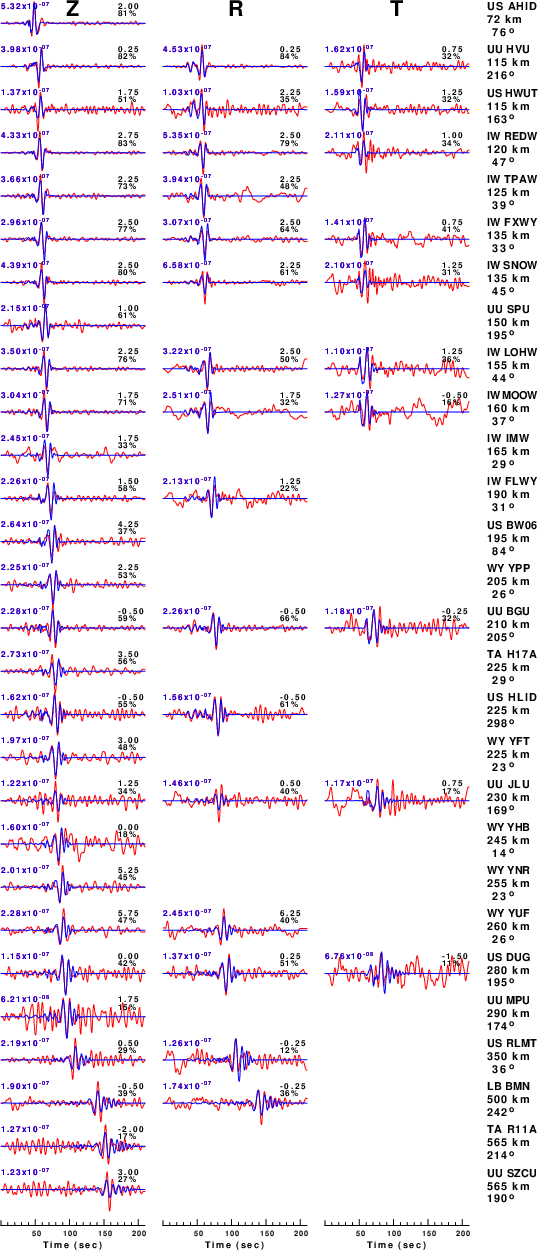
|
|
Figure 3. Waveform comparison for selected depth. Red: observed; Blue - predicted. The time shift with respect to the model prediction is indicated. The percent of fit is also indicated. The time scale is relative to the first trace sample.
|
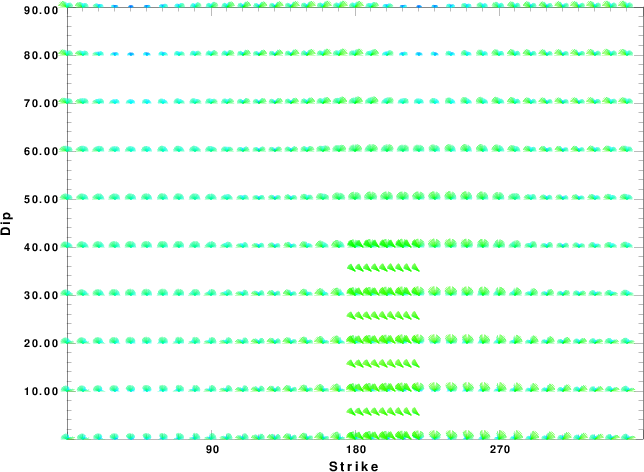
|
|
Focal mechanism sensitivity at the preferred depth. The red color indicates a very good fit to the waveforms.
Each solution is plotted as a vector at a given value of strike and dip with the angle of the vector representing the rake angle, measured, with respect to the upward vertical (N) in the figure.
|
A check on the assumed source location is possible by looking at the time shifts between the observed and predicted traces. The time shifts for waveform matching arise for several reasons:
- The origin time and epicentral distance are incorrect
- The velocity model used for the inversion is incorrect
- The velocity model used to define the P-arrival time is not the
same as the velocity model used for the waveform inversion
(assuming that the initial trace alignment is based on the
P arrival time)
Assuming only a mislocation, the time shifts are fit to a functional form:
Time_shift = A + B cos Azimuth + C Sin Azimuth
The time shifts for this inversion lead to the next figure:
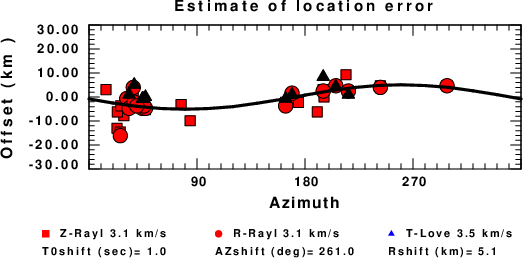
The derived shift in origin time and epicentral coordinates are given at the bottom of the figure.
Velocity Model
The WUS.model used for the waveform synthetic seismograms and for the surface wave eigenfunctions and dispersion is as follows
(The format is in the model96 format of Computer Programs in Seismology).
MODEL.01
Model after 8 iterations
ISOTROPIC
KGS
FLAT EARTH
1-D
CONSTANT VELOCITY
LINE08
LINE09
LINE10
LINE11
H(KM) VP(KM/S) VS(KM/S) RHO(GM/CC) QP QS ETAP ETAS FREFP FREFS
1.9000 3.4065 2.0089 2.2150 0.302E-02 0.679E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
6.1000 5.5445 3.2953 2.6089 0.349E-02 0.784E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
13.0000 6.2708 3.7396 2.7812 0.212E-02 0.476E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
19.0000 6.4075 3.7680 2.8223 0.111E-02 0.249E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
0.0000 7.9000 4.6200 3.2760 0.164E-10 0.370E-10 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
Last Changed Fri Apr 26 05:06:39 PM CDT 2024