Location
2014/04/13 12:11:30 -20.621 -70.715 18.6 5.3 Chile
Arrival Times (from USGS)
Arrival time list
Felt Map
USGS Felt map for this earthquake
USGS Felt reports main page
Focal Mechanism
USGS/SLU Moment Tensor Solution
ENS 2014/04/13 12:11:30:0 -20.62 -70.71 18.6 5.3 Chile
Stations used:
C.GO01 C.GO02 CX.MNMCX CX.PATCX CX.PB01 CX.PB04 CX.PB06
CX.PB07 CX.PB08 CX.PB09 CX.PB10 CX.PB11 CX.PB12 CX.PB14
CX.PB15 CX.PB16 CX.PSGCX GT.LPAZ IU.LVC
Filtering commands used:
cut a -30 a 180
rtr
taper w 0.1
hp c 0.02 n 3
lp c 0.06 n 3
Best Fitting Double Couple
Mo = 1.01e+24 dyne-cm
Mw = 5.27
Z = 20 km
Plane Strike Dip Rake
NP1 160 75 85
NP2 359 16 108
Principal Axes:
Axis Value Plunge Azimuth
T 1.01e+24 60 63
N 0.00e+00 5 161
P -1.01e+24 30 254
Moment Tensor: (dyne-cm)
Component Value
Mxx -4.20e+21
Mxy -9.67e+22
Mxz 3.20e+23
Myy -5.00e+23
Myz 8.12e+23
Mzz 5.04e+23
############--
----###############---
-------##################---
--------####################--
----------#####################---
-----------######################---
-------------######################---
--------------#######################---
---------------######### ##########---
----------------######### T ###########---
-----------------######## ###########---
-----------------######################---
----- ----------#####################---
---- P -----------###################---
---- -----------###################---
------------------#################---
------------------###############---
------------------#############---
-----------------###########--
------------------#######---
----------------###---
------------##
Global CMT Convention Moment Tensor:
R T P
5.04e+23 3.20e+23 -8.12e+23
3.20e+23 -4.20e+21 9.67e+22
-8.12e+23 9.67e+22 -5.00e+23
Details of the solution is found at
http://www.eas.slu.edu/eqc/eqc_mt/MECH.NA/20140413121130/index.html
|
Preferred Solution
The preferred solution from an analysis of the surface-wave spectral amplitude radiation pattern, waveform inversion and first motion observations is
STK = 160
DIP = 75
RAKE = 85
MW = 5.27
HS = 20.0
The NDK file is 20140413121130.ndk
The waveform inversion is preferred.
Moment Tensor Comparison
The following compares this source inversion to others
| SLU |
USGSMT |
USGS/SLU Moment Tensor Solution
ENS 2014/04/13 12:11:30:0 -20.62 -70.71 18.6 5.3 Chile
Stations used:
C.GO01 C.GO02 CX.MNMCX CX.PATCX CX.PB01 CX.PB04 CX.PB06
CX.PB07 CX.PB08 CX.PB09 CX.PB10 CX.PB11 CX.PB12 CX.PB14
CX.PB15 CX.PB16 CX.PSGCX GT.LPAZ IU.LVC
Filtering commands used:
cut a -30 a 180
rtr
taper w 0.1
hp c 0.02 n 3
lp c 0.06 n 3
Best Fitting Double Couple
Mo = 1.01e+24 dyne-cm
Mw = 5.27
Z = 20 km
Plane Strike Dip Rake
NP1 160 75 85
NP2 359 16 108
Principal Axes:
Axis Value Plunge Azimuth
T 1.01e+24 60 63
N 0.00e+00 5 161
P -1.01e+24 30 254
Moment Tensor: (dyne-cm)
Component Value
Mxx -4.20e+21
Mxy -9.67e+22
Mxz 3.20e+23
Myy -5.00e+23
Myz 8.12e+23
Mzz 5.04e+23
############--
----###############---
-------##################---
--------####################--
----------#####################---
-----------######################---
-------------######################---
--------------#######################---
---------------######### ##########---
----------------######### T ###########---
-----------------######## ###########---
-----------------######################---
----- ----------#####################---
---- P -----------###################---
---- -----------###################---
------------------#################---
------------------###############---
------------------#############---
-----------------###########--
------------------#######---
----------------###---
------------##
Global CMT Convention Moment Tensor:
R T P
5.04e+23 3.20e+23 -8.12e+23
3.20e+23 -4.20e+21 9.67e+22
-8.12e+23 9.67e+22 -5.00e+23
Details of the solution is found at
http://www.eas.slu.edu/eqc/eqc_mt/MECH.NA/20140413121130/index.html
|
Regional Moment Tensor (Mwr)
Moment magnitude derived from a moment tensor inversion
of complete waveforms at regional distances (less than
~8 degrees), generally used for the analysis of small
to moderate size earthquakes (typically Mw 3.5-6.0)
crust or upper mantle earthquakes.
Moment
1.12e+17 N-m
Magnitude
5.3
Percent DC
80%
Depth
15.0 km
Updated
2014-04-13 12:38:26 UTC
Author
us
Catalog
us
Contributor
us
Code
us_c000pipx_mwr
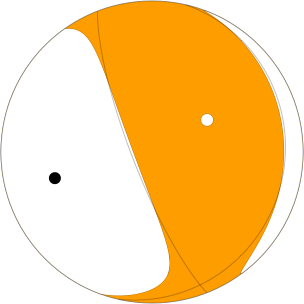
Principal Axes
Axis Value Plunge Azimuth
T 1.060 55 60
N 0.104 7 160
P -1.164 34 255
Nodal Planes
Plane Strike Dip Rake
NP1 159 79 83
NP2 13 13 123
|
|
Waveform Inversion
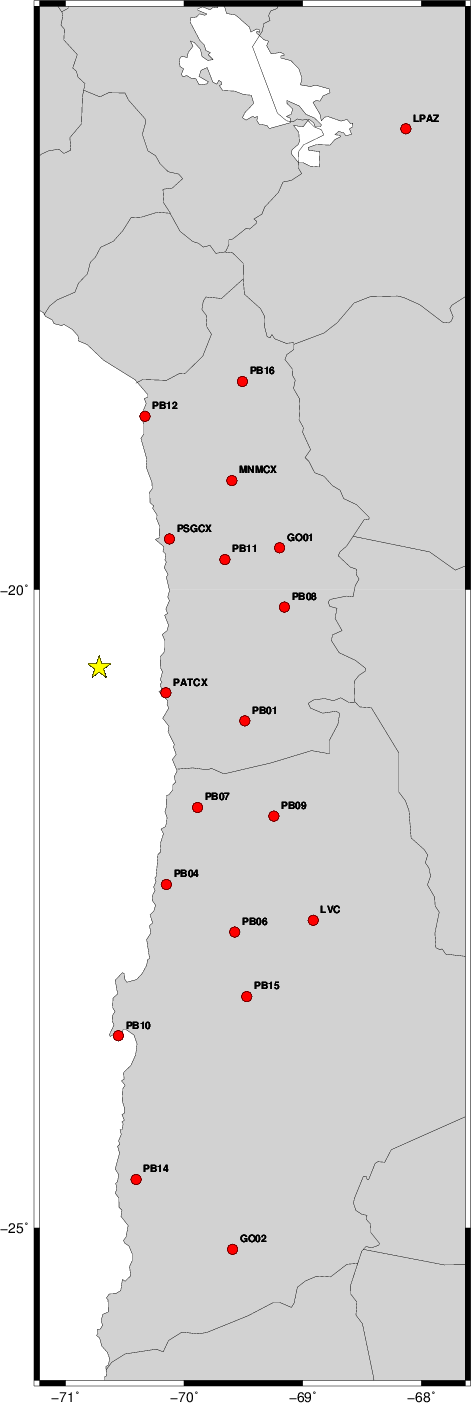
The focal mechanism was determined using broadband seismic waveforms. The location of the event and the
and stations used for the waveform inversion are shown in the next figure.
|
|
Location of broadband stations used for waveform inversion
|
The program wvfgrd96 was used with good traces observed at short distance to determine the focal mechanism, depth and seismic moment. This technique requires a high quality signal and well determined velocity model for the Green functions. To the extent that these are the quality data, this type of mechanism should be preferred over the radiation pattern technique which requires the separate step of defining the pressure and tension quadrants and the correct strike.
The observed and predicted traces are filtered using the following gsac commands:
cut a -30 a 180
rtr
taper w 0.1
hp c 0.02 n 3
lp c 0.06 n 3
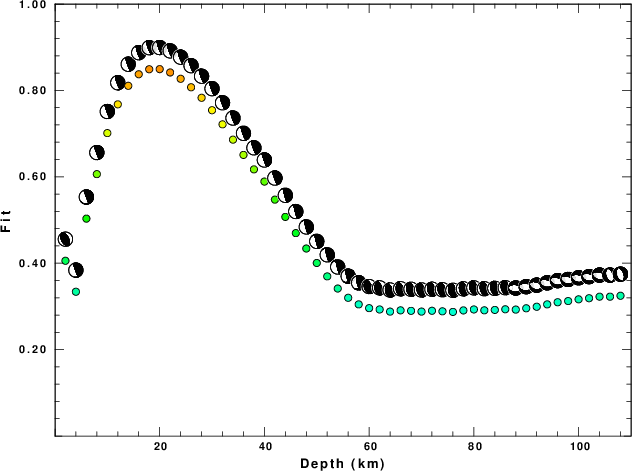
The results of this grid search from 0.5 to 19 km depth are as follow:
DEPTH STK DIP RAKE MW FIT
WVFGRD96 2.0 155 40 90 5.01 0.4057
WVFGRD96 4.0 160 85 85 5.12 0.3340
WVFGRD96 6.0 340 90 -85 5.12 0.5033
WVFGRD96 8.0 160 85 85 5.20 0.6062
WVFGRD96 10.0 160 85 85 5.21 0.7012
WVFGRD96 12.0 160 80 85 5.22 0.7678
WVFGRD96 14.0 160 80 85 5.24 0.8107
WVFGRD96 16.0 160 75 85 5.25 0.8374
WVFGRD96 18.0 160 75 85 5.26 0.8490
WVFGRD96 20.0 160 75 85 5.27 0.8493
WVFGRD96 22.0 160 75 90 5.30 0.8416
WVFGRD96 24.0 360 15 110 5.30 0.8270
WVFGRD96 26.0 345 10 95 5.32 0.8073
WVFGRD96 28.0 330 10 80 5.33 0.7830
WVFGRD96 30.0 325 10 75 5.34 0.7542
WVFGRD96 32.0 325 10 75 5.35 0.7215
WVFGRD96 34.0 330 10 80 5.35 0.6861
WVFGRD96 36.0 330 10 80 5.35 0.6508
WVFGRD96 38.0 160 80 90 5.35 0.6172
WVFGRD96 40.0 340 5 90 5.50 0.5890
WVFGRD96 42.0 340 5 90 5.50 0.5472
WVFGRD96 44.0 320 10 65 5.50 0.5073
WVFGRD96 46.0 320 10 65 5.50 0.4697
WVFGRD96 48.0 310 10 55 5.50 0.4341
WVFGRD96 50.0 310 10 55 5.50 0.4006
WVFGRD96 52.0 305 10 50 5.51 0.3695
WVFGRD96 54.0 295 10 40 5.51 0.3414
WVFGRD96 56.0 165 70 65 5.51 0.3200
WVFGRD96 58.0 165 70 65 5.52 0.3047
WVFGRD96 60.0 335 60 85 5.51 0.2960
WVFGRD96 62.0 335 60 80 5.52 0.2930
WVFGRD96 64.0 335 60 80 5.52 0.2880
WVFGRD96 66.0 175 35 105 5.53 0.2909
WVFGRD96 68.0 165 35 90 5.52 0.2898
WVFGRD96 70.0 165 35 90 5.53 0.2881
WVFGRD96 72.0 165 35 90 5.53 0.2899
WVFGRD96 74.0 165 35 90 5.54 0.2887
WVFGRD96 76.0 165 35 90 5.54 0.2873
WVFGRD96 78.0 170 40 95 5.55 0.2908
WVFGRD96 80.0 165 40 90 5.55 0.2930
WVFGRD96 82.0 345 50 90 5.55 0.2910
WVFGRD96 84.0 165 40 85 5.55 0.2919
WVFGRD96 86.0 165 40 85 5.55 0.2934
WVFGRD96 88.0 280 50 -80 5.56 0.2927
WVFGRD96 90.0 280 50 -80 5.56 0.2957
WVFGRD96 92.0 290 55 -80 5.57 0.2993
WVFGRD96 94.0 290 55 -80 5.57 0.3047
WVFGRD96 96.0 290 55 -80 5.57 0.3097
WVFGRD96 98.0 290 55 -80 5.58 0.3125
WVFGRD96 100.0 285 55 -85 5.59 0.3164
WVFGRD96 102.0 285 55 -85 5.59 0.3190
WVFGRD96 104.0 285 55 -85 5.59 0.3226
WVFGRD96 106.0 340 50 -90 5.60 0.3226
WVFGRD96 108.0 165 40 -85 5.60 0.3247
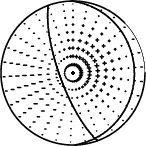
The best solution is
WVFGRD96 20.0 160 75 85 5.27 0.8493
The mechanism correspond to the best fit is
|
|
Figure 1. Waveform inversion focal mechanism
|
The best fit as a function of depth is given in the following figure:
|
|
Figure 2. Depth sensitivity for waveform mechanism
|
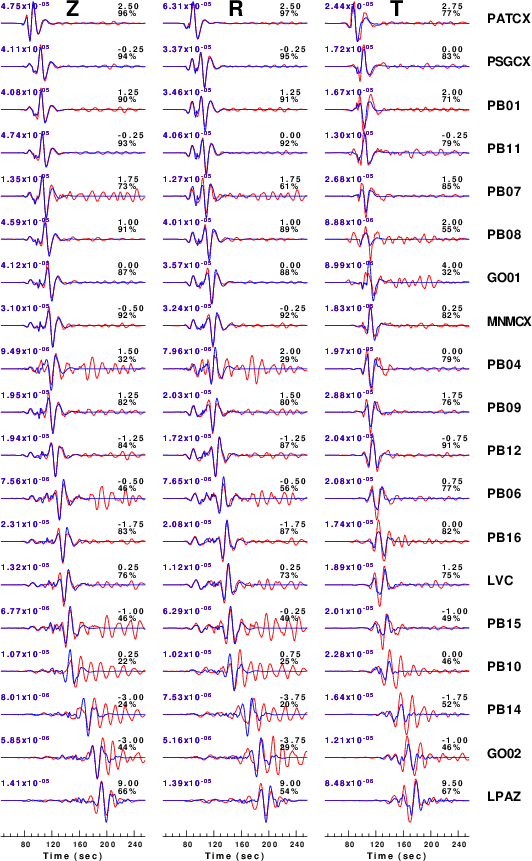
The comparison of the observed and predicted waveforms is given in the next figure. The red traces are the observed and the blue are the predicted.
Each observed-predicted component is plotted to the same scale and peak amplitudes are indicated by the numbers to the left of each trace. A pair of numbers is given in black at the right of each predicted traces. The upper number it the time shift required for maximum correlation between the observed and predicted traces. This time shift is required because the synthetics are not computed at exactly the same distance as the observed and because the velocity model used in the predictions may not be perfect.
A positive time shift indicates that the prediction is too fast and should be delayed to match the observed trace (shift to the right in this figure). A negative value indicates that the prediction is too slow. The lower number gives the percentage of variance reduction to characterize the individual goodness of fit (100% indicates a perfect fit).
The bandpass filter used in the processing and for the display was
cut a -30 a 180
rtr
taper w 0.1
hp c 0.02 n 3
lp c 0.06 n 3
|
|
Figure 3. Waveform comparison for selected depth. Red: observed; Blue - predicted. The time shift with respect to the model prediction is indicated. The percent of fit is also indicated.
|
|
|
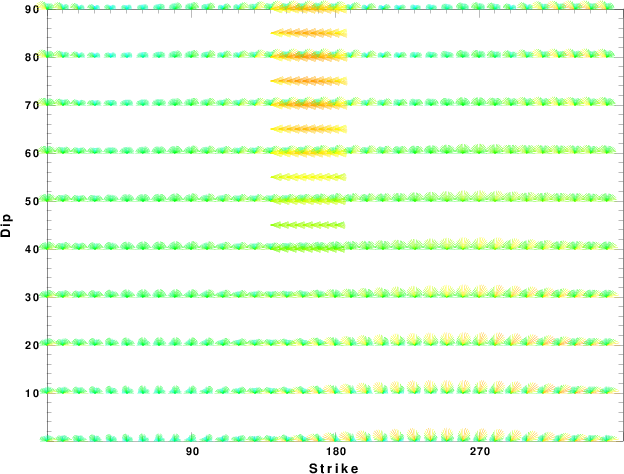
Focal mechanism sensitivity at the preferred depth. The red color indicates a very good fit to thewavefroms.
Each solution is plotted as a vector at a given value of strike and dip with the angle of the vector representing the rake angle, measured, with respect to the upward vertical (N) in the figure.
|
A check on the assumed source location is possible by looking at the time shifts between the observed and predicted traces. The time shifts for waveform matching arise for several reasons:
- The origin time and epicentral distance are incorrect
- The velocity model used for the inversion is incorrect
- The velocity model used to define the P-arrival time is not the
same as the velocity model used for the waveform inversion
(assuming that the initial trace alignment is based on the
P arrival time)
Assuming only a mislocation, the time shifts are fit to a functional form:
Time_shift = A + B cos Azimuth + C Sin Azimuth
The time shifts for this inversion lead to the next figure:
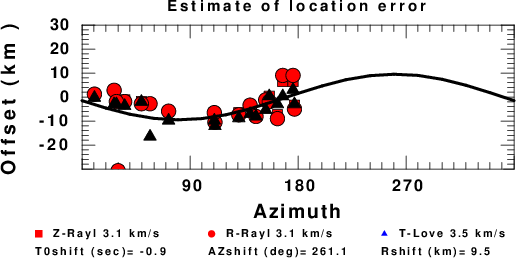
The derived shift in origin time and epicentral coordinates are given at the bottom of the figure.
Discussion
Acknowledgements
Thanks also to the many seismic network operators whose dedication make this effort possible: University of Nevada Reno, University of Alaska, University of Washington, Oregon State University, University of Utah, Montana Bureas of Mines, UC Berkely, Caltech, UC San Diego, Saint Louis University, University of Memphis, Lamont Doherty Earth Observatory, the Iris stations and the Transportable Array of EarthScope.
Velocity Model
The WUS used for the waveform synthetic seismograms and for the surface wave eigenfunctions and dispersion is as follows:
MODEL.01
Model after 8 iterations
ISOTROPIC
KGS
FLAT EARTH
1-D
CONSTANT VELOCITY
LINE08
LINE09
LINE10
LINE11
H(KM) VP(KM/S) VS(KM/S) RHO(GM/CC) QP QS ETAP ETAS FREFP FREFS
1.9000 3.4065 2.0089 2.2150 0.302E-02 0.679E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
6.1000 5.5445 3.2953 2.6089 0.349E-02 0.784E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
13.0000 6.2708 3.7396 2.7812 0.212E-02 0.476E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
19.0000 6.4075 3.7680 2.8223 0.111E-02 0.249E-02 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
0.0000 7.9000 4.6200 3.2760 0.164E-10 0.370E-10 0.00 0.00 1.00 1.00
Quality Control
Here we tabulate the reasons for not using certain digital data sets
The following stations did not have a valid response files:
Last Changed Sun Apr 13 10:15:47 CDT 2014






