The new programs are as follow:
The programs are controlled by command line arguments. The options for hpulse96strain and spulse96strain are extensive to permit different formats for output file naming.
Before illustrating the computation sequence of the new codes, the following show the sequence making synthetic displacement, velocity or acceleration time histories. This is the sequence that is used in the validation scripts int he WK and SW directories.
| Wavenumber Integration | Modal Superposition |
|---|---|
hprep96 -d dfile -M CUS.mod -HS 10.0 -HR 3.0 hspec96 hpulse96 -V -p -l 1 | f96tosac -Gfor isotropic material, and
hprep96 -d dfile -M CUS.mod -HS 10.0 -HR 3.0 tspec96 hpulse96 -V -p -l 1 | f96tosac -Gfor transverse isotropic media. |
sprep96 -d dfile -M CUS.mod -HS 10.0 -HR 3.0 -L -R -NMOD 100 sdisp96 sregn96 slegn96 spulse96 -V -p -l 1 | f96tosac -G |
The output at this stage is a set of Green's functions of the form 050000100.XXX, where the XXX indicates the particular Green's function and is one of ZDD, RDD, ZDS, RDS, ZSS, RSS, TSS, ZEX, REX, ZVF, RVF, ZHF, RHF or THF. To create the three component time series for the displacement/velocity/acceleration, the gsac mt command is used. An illustration of this is in the file CPSstrain.validate/WKkm/DOSTRAIN.
The new codes compute the three component motion or strain/stress/rotation for a given mechanism. Thus they cannot be used with the gsac mt command. The complete sequence using the new codes is similar to that used above. The example scripts for wavenumber integration are CPSstrain.validate/WK/DOITWK for a moment tensor source and CPSstrain.validate/WK/DOITWKF for a point force source. The corresponding scripts for modal superposition are CPSstrain.validate/SW/DOITSW for a moment tensor source and CPSstrain.validate/SW/DOITSWF for a point force source.
The following shows the sequence of operations:
| Wavenumber Integration | Modal Superposition |
|---|---|
hprep96 -d dfile -M CUS.mod -HS 10.0 -HR 3.0
hspec96strain
hpulse96strain -V -p -l 1 -MW ${MW} -STK ${STK} -DIP ${DIP} \\
-RAKE ${RAKE} -AZ ${AZ} -STRESS -STRAIN -ROTATE -FMT 1
for isotropic models, and
hprep96 -d dfile -M CUS.mod -HS 10.0 -HR 3.0
tspec96strain
hpulse96strain -V -p -l 1 -MW ${MW} -STK ${STK} -DIP ${DIP} \\
-RAKE ${RAKE} -AZ ${AZ} -STRESS -STRAIN -ROTATE -FMT 1
for transverse isotropic models.
|
sprep96 -d dfile -M CUS.mod -HS 10.0 -HR 3.0 -L -R -NMOD 100
sdisp96
sregn96
slegn96
spulse96strain -V -p -l 1 -d dfile -MW ${MW} -STK ${STK} -DIP ${DIP} \\
-RAKE ${RAKE} -AZ ${AZ} -STRESS -STRAIN -ROTATE -FMT 1
|
In the scripts the shell variables STK, DIP, RAKE, AZ and MW specify the source parameters. The command line parameters of hspec96strain are the same as those if hspec96. The hpulse96strain combines the functions of hpulse96, f96tosac, fmech96 and the mt command of gsac and likewise of spulse96strain.
When the -STRAIN is invoked with the -FMT 1 flag,, the output will be Sac files with names such as
002000_0100_0050.Eff 002000_0100_0050.Erf 002000_0100_0050.Erz 002000_0100_0050.Efz 002000_0100_0050.Err 002000_0100_0050.Ezz 002000_0100_0050.DelThe units are strain, and not microstrain or nanostrain
If the -STRESS is invoked, the output Sac files will be of the form
002000_0100_0050.Sff 002000_0100_0050.Srf 002000_0100_0050.Srz 002000_0100_0050.Sfz 002000_0100_0050.Srr 002000_0100_0050.Szzwith units of Pa.
If the -ROTATE is given, the output will be
002000_0100_0050.Wfz 002000_0100_0050.Wrf 002000_0100_0050.Wrzwith units of m/m.
Finally if the -D, -V or -A is given, the following result:
002000_0100_0050.Ur 002000_0100_0050.Ut 002000_0100_0050.Uzwhere these are m, m/s or m/s/s, respectively. The only non-standard point is the Z is positive downward rather than positive upward. This is not a problem since I would use the hpulse96 sequence and gsac to compute the 3-component motion.
To get the units just mentioned, the model file must be in terms of km, km/s and gm/cm3.
To get the units just mentioned, the model file must be in terms of km, km/s and gm/cm3.
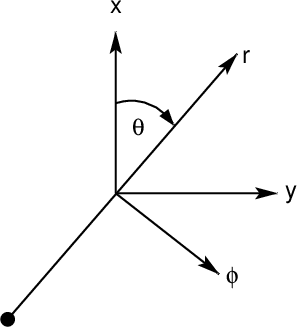
Note that everything is in terms of a cylindrical coordinate system. In modeling data, it is natural to specify the epicenter and then compute the motions at the receiver with is at (r,φ) with respect to the source. The instruments may not be aligned in the
If the computational run gave the files starting with 002000_0100_0050, then the command
srotate96 -U -STRESS -STRAIN -ROTATE -AZ 30 -FILE 002000_0100_0050gives
2000_0100_0050_Exx 002000_0100_0050_Eyy 002000_0100_0050_Sxx 002000_0100_0050_Syy 002000_0100_0050_Wxy 002000_0100_0050_Exy 002000_0100_0050_Eyz 002000_0100_0050_Sxy 002000_0100_0050_Syz 002000_0100_0050_Wxz 002000_0100_0050_Exz 002000_0100_0050_Ezz 002000_0100_0050_Sxz 002000_0100_0050_Szz 002000_0100_0050_WyzNote the use of the underscore instead of the period.
USAGE: hspec96strain [-H] [-A arg] [-K] [-N][-SU] [-SD] [-SPUP] [-SSUP] [-SPDN] [-SSDN] [-RU] [-RD] [-RPUP] [-RSUP] [-RPDN] [-RSDN] [-?] [-h]
-H (default false) Use Hankel function not Bessel
-A arg (default arg=3.0) value of kr where Hn(kr) replaces
Jn(kr) in integration - only used when -H is used
-K (default Futterman) use Kjartansson Causal Q
-N (default causal) use non-causal Q
The following govern wavefield at source. The default is the entire wavefield
-SU (default whole wavefield) Compute only upgoing wavefield from the source
-SD (default whole wavefield) Compute only downgoing wavefield from the source
-SPUP Include upward P at source
-SSUP Include upward S at source
-SPDN Include downward P at source
-SSDN Include downward S at source
The following govern wavefield at receiver. The default is the entire wavefield
-RD Only downgoing waves at receiver
-RU Only upgoing waves at receiver
-RPUP Include upward P at receiver
-RSUP Include upward S at receiver
-RPDN Include downward P at receiver
-RSDN Include downward S at receiver
-? Display this usage message
-h Display this usage message
USAGE: tspec96strain [-H] [-A arg] [-K] [-SU] [-SD] [-SPUP] [-SSUP] [-SPDN] [-SSDN] [-RU] [-RD] [-RPUP] [-RSUP] [-RPDN] [-RSDN] [-?] [-h]
-H (default false) Use Hankel function not Bessel
-A arg (default arg=3.0) value of kr where Hn(kr) replaces
Jn(kr) in integration - only used when -H is used
-K (default Futterman) use Kjartansson Causal Q
The following govern wavefield at source. The default is the entire wavefield
-SU (default whole wavefield) Compute only upgoing wavefield from the source
-SD (default whole wavefield) Compute only downgoing wavefield from the source
-SPUP Include upward P at source
-SSUP Include upward S at source
-SPDN Include downward P at source
-SSDN Include downward S at source
The following govern wavefield at receiver. The default is the entire wavefield
-RD Only downgoing waves at receiver
-RU Only upgoing waves at receiver
-RPUP Include upward P at receiver
-RSUP Include upward S at receiver
-RPDN Include downward P at receiver
-RSDN Include downward S at receiver
-? Display this usage message
-h Display this usage message
hpulse96strain:Help
USAGE:
hpulse96strain -d Distance_File [ -t -o -p -i ] [-a alpha]
-l L [ -D|-V |A] [-F rfile ] [ -m mult] [-STEP|-IMP]
[-STRESS -STRAIN -ROTATE -GRN] [-FUND] [-HIGH] [-Z]
[-LAT] [-2] [ -M mode ] [-LOCK] -FMT ifmt
[-M0 moment ] [-MW mw] [-STK stk -DIP dip -RAKE rake]
[-FX fx -FY fy -FZ fz]
[-XX Mxx ... -ZZ Mzz] [-?] [-h]
TIME FUNCTION SPECIFICATION
-t Triangular pulse of base 2 L dt
-p Parabolic Pulse of base 4 L dt
-p -l 1 recommended
-l L (default 1 )duration control parameter
-o Ohnaka pulse with parameter alpha
-i Dirac Delta function
-a alpha Shape parameter for Ohnaka pulse
-F rfile User supplied pulse
-m mult Multiplier (default 1.0)
-STEP (default)
-IMP
By default the source time function is
steplike. -IMP forces impulse like. -D -IMP is Green s function
OUTPUT FILE NAME
The format for the name of the binary output attempts to
give information on epicentral distance (km),
source depth (km), and receiver depth(km). The options are
-FMT 1 DDDDDd_HHHh_ZZZz.cmp
e.g. 005001_1234_0045.Uz
-FMT 2 DDDDDddd_HHHhhh_ZZZzzz.cmp
e.g. 00500123_123456_004578.Erf
-FMT 3 DDDDDdHHHh.grn(default)
e.g. 0050010041.ZVF
-FMT 4 DDDDdHHHh.grn
e.g. 050010045.Srz
-FMT 5 DDDdddHhhh.grn
e.g. 5001234578.Err
where D is for epicentral distance, H source depth, and
Z receiver depth. The lower case indicates the digits
to the right of the decimal place. The examples above
are for an epicentral distance is 500.123 km, source
depth 123.456 km and receiver depth 4.578 km.
OUTPUT TIMESERIES FOR SOURCE as Ur, Ut, Uz components with strain, stress optional
-D Output is ground displacement (m)
-V Output is ground velocity (default) (m/s)
-A Output is ground acceleration (m/s^2)
-STRESS (default .false. ) output stress for mechanism
units are Pa, with suffix Srr, Srf, Srz, Stt, Sfz, Szz
-STRAIN (default .false. ) output strain for mechanism
with suffix, Err, Erf, Erz, Eff, Efz, Ezz
-ROTATE (default .false. ) output rotation for mechanism
with suffix, Wfz, Wrz, Wrf
-GRN (default false) Output Green;s functions
hpulse96strain -STEP -V -p -l 1 -GRN -FMT 4 is same as
hpulse96 -V -p -l 1 | f96tosac -G . For KM,KM/S,GM/CM^3
model, output will be CM/S for moment of 1.0e+20 dyne-cm
of force of 1.0e+15 dyne
-TEST1 (default .false.) output CPS Green functions ,e.g.,
ZDS RDS ... RHF THF for use with moment tensor codes
and gsac MT command. This is equivalent to
hpulse96 -V -p -l 1 | f96tosac -G if -FMT 4 is used
with hpulse96strain
COMPUTATIONS
-Z (default false) zero phase
SOURCE MECHANISM SPECIFICATION
-DIP dip dip of fault plane
-STK Strike strike of fault plane
-RAKE Rake slip angle on fault plane
-M0 Moment (def=1.0) Seismic moment in units of dyne-cm
-MW mw Moment Magnitude
moment (dyne-cm) from log10 Mom = 16.10 + 1.5 Mw
For strike,dip,rake source mw or Moment must be specified
-EX Explosion
-AZ Az Source to Station Azimuth
-BAZ Baz Station to Source azimuth
-fx FX -fy Fy -fZ fz Point force amplitudes (N,E,down) in dynes
-XX Mxx -YY Myy -ZZ Mzz Moment tensor elements in units of
-XY Mxy -XZ Mxz -YZ Myz dyne-cm
The moment tensor coordinates are typically X = north Y = east and Z = down
If by accident more than one source specification is used,
the hierarchy is Mij > Strike,dip,rake > Explosion > Force
--------------------------------------------------------------
NOTE: The output units are related tot he model specification.
To have the desired units the model must be in KM, KM/S and GM/CM^3
--------------------------------------------------------------
-? Write this help message
-h Write this help message
spulse96strain:Help
USAGE:
spulse96strain -d Distance_File [ -t -o -p -i ] [-a alpha]
-l L [ -D|-V |A] [-F rfile ] [ -m mult] [-STEP|-IMP]
[-STRESS -STRAIN -ROTATE -GRN] [-FUND] [-HIGH] [-Z]
[-LAT] [-2] [ -M mode ] [-LOCK] -FMT ifmt
[-M0 moment ] [-MW mw] [-STK stk -DIP dip -RAKE rake]
[-FX fx -FY fy -FZ fz]
[-XX Mxx ... -ZZ Mzz] [-?] [-h]
TIME FUNCTION SPECIFICATION
-t Triangular pulse of base 2 L dt
-p Parabolic Pulse of base 4 L dt
-p -l 1 recommended
-l L (default 1 )duration control parameter
-o Ohnaka pulse with parameter alpha
-i Dirac Delta function
-a alpha Shape parameter for Ohnaka pulse
-F rfile User supplied pulse
-m mult Multiplier (default 1.0)
-STEP (default)
-IMP
By default the source time function is
steplike. -IMP forces impulse like. -D -IMP is Green s function
OUTPUT FILE NAME
The format for the name of the binary output attempts to
give information on epicentral distance (km),
source depth (km), and receiver depth(km). The options are
-FMT 1 DDDDDd_HHHh_ZZZz.cmp
e.g. 005001_1234_0045.Uz
-FMT 2 DDDDDddd_HHHhhh_ZZZzzz.cmp
e.g. 00500123_123456_004578.Erf
-FMT 3 DDDDDdHHHh.grn(default)
e.g. 0050010041.ZVF
-FMT 4 DDDDdHHHh.grn
e.g. 050010045.Srz
-FMT 5 DDDdddHhhh.grn
e.g. 5001234578.Err
where D is for epicentral distance, H source depth, and
Z receiver depth. The lower case indicates the digits
to the right of the decimal place. The examples above
are for an epicentral distance is 500.123 km, source
depth 123.456 km and receiver depth 4.578 km.
OUTPUT TIMESERIES FOR SOURCE as Ur, Ut, Uz components with strain, stress optional
-D Output is ground displacement (m)
-V Output is ground velocity (default) (m/s)
-A Output is ground acceleration (m/s^2)
-STRESS (default .false. ) output stress for mechanism
units are Pa, with suffix Srr, Srf, Srz, Stt, Sfz, Szz
-STRAIN (default .false. ) output strain for mechanism
with suffix, Err, Erf, Erz, Eff, Efz, Ezz
-ROTATE (default .false. ) output rotation for mechanism
with suffix, Wfz, Wrz, Wrf
-GRN (default false) Output Green;s functions
spulse96strain -STEP -V -p -l 1 -GRN -FMT 4 is same as
spulse96 -V -p -l 1 | f96tosac -G . For KM,KM/S,GM/CM^3
model, output will be CM/S for moment of 1.0e+20 dyne-cm
of force of 1.0e+15 dyne
-TEST1 (default .false.) output CPS Green functions ,e.g.,
ZDS RDS ... RHF THF for use with moment tensor codes
and gsac MT command. This is equivalent to
spulse96 -V -p -l 1 | f96tosac -G if -FMT 4 is used
with strainspulse96
COMPUTATIONS
-d Distance_File {required} Distance control file
This contains one of more lines with following entries
DIST(km) DT(sec) NPTS T0(sec) VRED(km/s)
first time point is T0 + DIST/VRED
VRED=0 means do not use reduced travel time, e.g.
500.0 0.25 512 -23.33 6.0
500.0 0.25 512 60 0.0
both have first sample at travel time of 60s
-LAT (default false) Laterally varying eigenfunctions
-2 (default false) Use double length internally
-M nmode (default all) mode to compute [0=fund,1=1st]
-Z (default false) zero phase triangular/parabolic pulse
-FUND (default all) fundamental modes only
-HIGH (default all) all higher modes only
-LOCK (default false) locked mode used
SOURCE MECHANISM SPECIFICATION
-DIP dip dip of fault plane
-STK Strike strike of fault plane
-RAKE Rake slip angle on fault plane
-M0 Moment (def=1.0) Seismic moment in units of dyne-cm
-MW mw Moment Magnitude
moment (dyne-cm) from log10 Mom = 16.10 + 1.5 Mw
For strike,dip,rake source mw or Moment must be specified
-EX Explosion
-AZ Az Source to Station Azimuth
-BAZ Baz Station to Source azimuth
-fx FX -fy Fy -fZ fz Point force amplitudes (N,E,down) in dynes
-XX Mxx -YY Myy -ZZ Mzz Moment tensor elements in units of
-XY Mxy -XZ Mxz -YZ Myz dyne-cm
The moment tensor coordinates are typically X = north Y = east and Z = down
If by accident more than one source specification is used,
the hierarchy is Mij > Strike,dip,rake > Explosion > Force
--------------------------------------------------------------
NOTE: The output units are related tot he model specification.
To have the desired units the model must be in KM, KM/S and GM/CM^3
--------------------------------------------------------------
-? Write this help message
-h Write this help message
Usage: srotate96 -AZ az [-U|-STRESS|-STRAIN] -FILE prototype
-AZ az (required) angle between r- and x-axes
-FILE prototype (required) identifier for filename
for the example below this could be ../NEW/005000_0100_0010
-U Rotate the Ur Ut Uz from [sh]pulse96strain to Ux Uy Uz
if they exist, e.g., ../NEW/005000_0100_0010.Ur etc
to create 005000_0100_0010_Ux etc in the current directory
-STRAIN Rotate the Err Erf .. Ezz from [sh]pulse96strain to Exx Eyy ..
if they exist, e.g., ../NEW/005000_0100_0010.Err etc
to create 005000_0100_0010_Exx etc in the current directory
-STRESS Rotate the Srr Srf .. Szz from [sh]pulse96strain to Sxx Syy ..
if they exist, e.g., ../NEW/005000_0100_0010.Srr etc
to create 005000_0100_0010_Sxx etc in the current directory
-ROTATE Rotate the Wrf Wrz Wfz from [sh]pulse96strain to Wxy Wxz Wyz
if they exist, e.g., ../NEW/005000_0100_0010.Wrf etc
to create 005000_0100_0010_Wxy etc in the current directory
-h (default false) online help